Heat Maps and Vibrations: The Importance of Thermal and Frequency Analysis in Engineering
- mohibraid

- Feb 15, 2024
- 2 min read
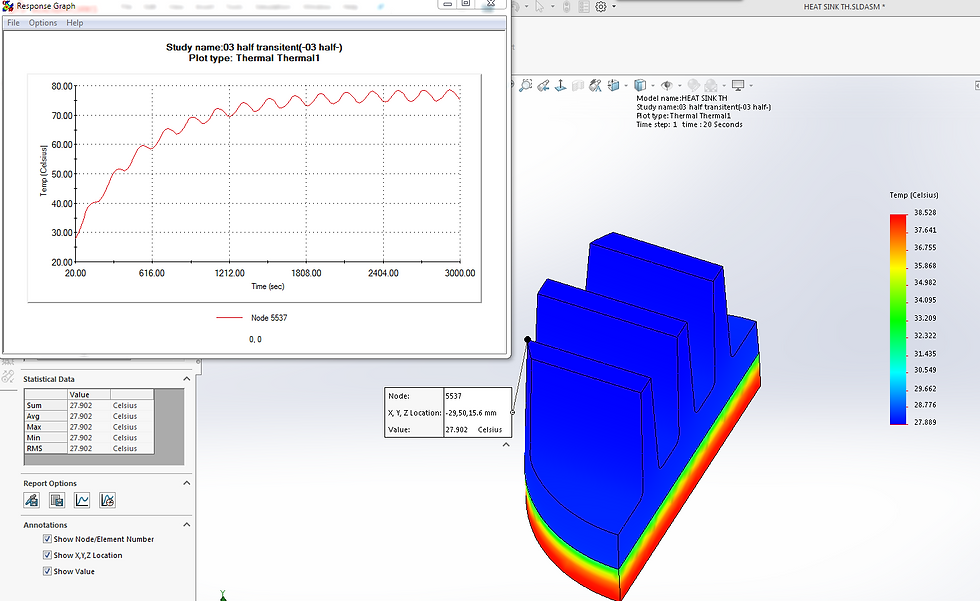
In the dynamic field of engineering, understanding how materials and structures respond to thermal and vibrational loads is crucial for ensuring performance, reliability, and safety. Engineers employ two effective methods to study these phenomena: thermal analysis and frequency analysis. This article explores the significance of thermal and frequency analysis in engineering, their applications across industries, and how they aid in system design, optimization, and validation.
Understanding Thermal Analysis:
Thermal analysis investigates material and structural behavior under heat transfer scenarios, predicting temperature distributions, thermal gradients, and heat fluxes. This method is pivotal across engineering disciplines, including mechanical, aerospace, automotive, and electronics.
Key Aspects of Thermal Analysis:
Heat Transfer Modes: Thermal analysis considers various modes of heat transfer—conduction, convection, and radiation. Engineers use mathematical models and simulations to quantify heat transfer rates and predict temperature variations within components.
Material Properties: Material properties such as thermal conductivity and expansion coefficient significantly influence thermal behavior. Accurate characterization of these properties is crucial for reliable thermal analysis.
Boundary Conditions: Establishing boundary conditions, such as heat sources and insulation, defines the thermal environment. Engineers use boundary conditions to simulate realistic operating conditions and assess thermal performance accurately.
Transient Effects: Dynamic thermal analysis examines transient thermal effects, including startup/shutdown scenarios and transient heat sources. Engineers analyze potential thermal loads, fatigue, and deformation over time.
Applications of Thermal Analysis:
Electronics Cooling: Thermal analysis optimizes electronic systems' cooling and thermal management to prevent overheating and failure.
Aerospace Structures: Thermal analysis ensures structural integrity and thermal protection in extreme environments.
Automotive Systems: Thermal analysis enhances vehicle performance, reliability, and passenger comfort.
Industrial Processes: Thermal analysis optimizes processes such as metal casting and welding to improve product quality and efficiency.
Understanding Frequency Analysis:
Frequency analysis studies structures' dynamic behavior under mechanical excitations, determining natural frequencies, mode shapes, and damping properties.
Key Aspects of Frequency Analysis:
Natural Frequencies: Frequency analysis identifies natural frequencies, critical for understanding resonance and vibration modes.
Mode Shapes: Engineers visualize mode shapes to comprehend how structures deform and oscillate under dynamic loading.
Damping Effects: Frequency analysis evaluates damping properties to quantify energy dissipation and forecast dynamic response.
Forced Response Analysis: Engineers use forced response analysis to assess vibration-induced stresses and fatigue life in engineering systems.
Applications of Frequency Analysis:
Structural Dynamics: Frequency analysis ensures structural safety and reliability in civil structures.
Machinery and Equipment: Frequency analysis optimizes machinery performance and prevents premature failure.
Automotive Dynamics: Frequency analysis enhances vehicle dynamics and ride comfort.
Aerospace Structures: Frequency analysis ensures stability and reliability in aerospace systems.
Integration of Thermal and Frequency Analysis:
Integrating thermal and frequency analysis enables engineers to assess the coupled effects of thermal loads and vibrational excitations, optimizing thermal management and enhancing structural integrity.
Conclusion:
Thermal and frequency analysis are indispensable tools in engineering, offering crucial insights into material behavior and structural dynamics. By leveraging these methods, engineers can design innovative solutions and ensure the performance, reliability, and safety of complex systems.




Comments